
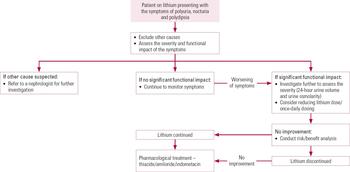
Clinical features: polyuria, nocturia, and polydipsia → ↑ risk of dehydrationand subsequent lithium toxicity.Pathophysiology: lithium interferes with ADH signaling → ↓ aquaporins (water channels) on the collecting duct cell's surface → ↓ water molecules are reabsorbed and kidneys are unable to concentrate urine → ↑ free water excretion.Goiter (particularly in second and third trimester of pregnancy ).Caused by the elevation of the calcium-sensing setpoint of the parathyroid glands and induction of parathyroid hormone production.

There is usually no need to discontinue lithium therapy.Lithium-induced hypothyroidism, should be treated with replacement therapy ( levothyroxine).



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
